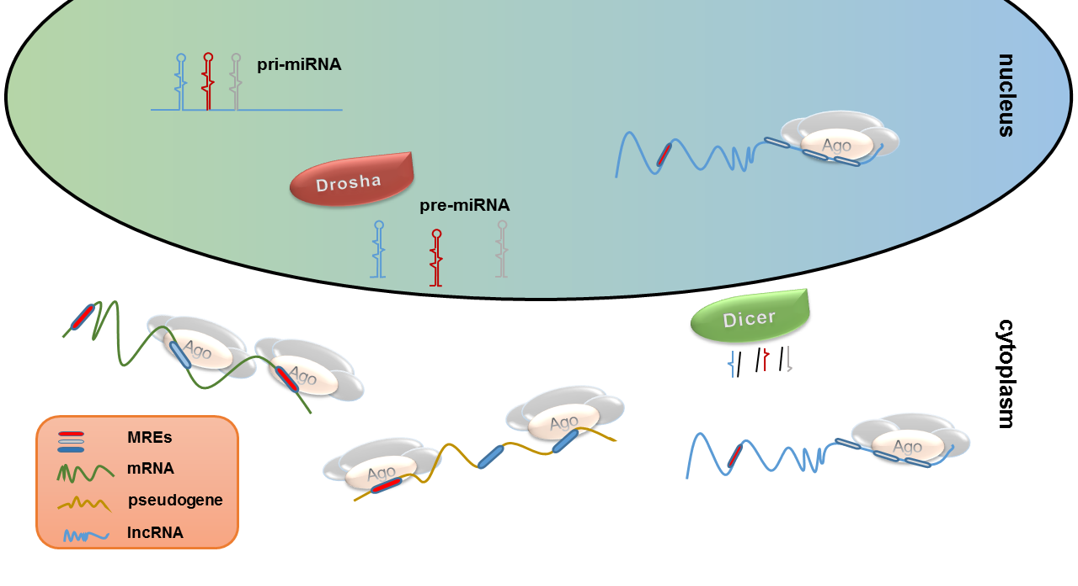
MicroRNA research represents a groundbreaking field that has reshaped our understanding of gene regulation, particularly through the pioneering work of Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun. His studies, notably involving the C. elegans roundworm, unveiled the critical roles these small RNA molecules play in biological processes. Initially met with skepticism, Ruvkun and Victor Ambros’s discovery eventually garnered significant attention, eventually earning them the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024. This revelation has spurred further investigation into the therapeutic potential of microRNAs, with ongoing clinical trials exploring their application in treating diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease. With robust federal funding underpinning this vital research, the implications of microRNA extend far beyond the lab, impacting modern medicine and our approach to gene therapy.
The exploration of microRNAs—tiny yet powerful regulators of gene expression—has opened new avenues in genetic research and therapeutic development. After their initial discovery in the early 1990s, these small molecules have proven essential not only in the model organism C. elegans but also across species, including humans. As research evolves, the significance of microRNA in the contexts of disease and developmental biology continues to grow, prompting investment and interest from both the scientific community and biotech industries. Through innovation and the support of federal funding for scientific investigations, the journey of microRNAs illustrates a transformative chapter in genetics, one that is crucial for advancing our understanding of health and disease.
The Journey of microRNA Research: From Discovery to Nobel Prize
Gary Ruvkun’s pioneering work on microRNA, initially seen as a mere curiosity, has profoundly reshaped our understanding of gene regulation. His discovery in 1992 alongside Victor Ambros marked a turning point, leading to their eventual recognition with the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Their research into the C. elegans roundworm illuminated the groundbreaking role microRNAs play in gene expression, but it took years for the broader biological community to grasp the significance of their findings.
Over the decades, initial skepticism transformed into fervent interest, as subsequent studies revealed that microRNAs are not exclusively significant in C. elegans but are critical in various species, including humans. This has opened new avenues for understanding complex biological processes and has underscored the relevance of federally funded microRNA research in today’s biomedical landscape.
The Role of Federal Funding in Advancing Scientific Research
Federal funding has been instrumental in supporting Gary Ruvkun’s research over the years, demonstrating the vital role government investment plays in advancing scientific inquiry. Approximately three-quarters of Ruvkun’s lab’s funding has come from federal sources, which has enabled him to employ a dedicated team of researchers. This financial support is critical, especially in a field as dynamic and rapidly evolving as microRNA research, where funding not only supports salaries but also the infrastructure required for groundbreaking studies.
However, Ruvkun has expressed concern about the political climate surrounding scientific funding. Calls to reduce federal investments could jeopardize future advancements in the field and discourage young scientists from pursuing research careers. The continuity of support for research is essential not only for the development of innovative therapies but for maintaining the United States’ position as a leader in scientific discovery.
Clinical Trials: The Impact of microRNA on Modern Medicine
The ongoing clinical trials exploring microRNA-based therapies represent a significant breakthrough in modern medicine. Potential treatments targeting conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases underscore the therapeutic possibilities that microRNAs offer. This approach to gene regulation has the potential to revolutionize how we treat these ailments, providing new hope for patients and opening doors for personalized medicine.
As researchers continue to study the mechanisms behind microRNAs, the data generated from clinical trials is crucial. It not only validates the roles of microRNAs in human health but also provides a roadmap for the development of future RNA-based therapeutics. The foundation laid by Ruvkun and Ambros’ initial discovery is now leading to tangible outcomes that could drastically improve patient care and treatment efficacy.
The Significance of Gene Regulation in Evolutionary Biology
Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNA has illuminated the intricate mechanisms of gene regulation, significantly impacting our understanding of evolutionary biology. By studying microRNAs in C. elegans, Ruvkun and others have unveiled how gene expression is fine-tuned and adapted throughout evolution. This understanding is pivotal as it helps explain the variability and adaptability of organisms in response to environmental changes.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic biology. By understanding gene regulation through the lens of microRNAs, scientists can better comprehend the evolutionary pressures that shape life forms on Earth. This knowledge contributes to the broader field of evolutionary genetics, providing insights into how organisms have developed diverse traits and functionalities.
The Broader Implications of RNA Research
The exponential growth of interest in RNA research stems from its significant implications in understanding cellular processes. The discovery of microRNAs added a critical layer to our comprehension of gene expression and regulation, highlighting their relevance across various biological systems, from plants to humans. This paradigm shift has sparked collaborations across disciplines and broadened the focus of genetic research to include small RNA molecules.
As researchers uncover more about the roles of microRNAs, the potential applications in agriculture, biotechnology, and medicine become more evident. Innovations in RNA research not only enhance our understanding but also open doors for novel therapeutic strategies and agricultural improvements, significantly impacting global health and food security.
The Evolution of Scientific Communities Focused on RNA Research
Initially, the microRNA community was relatively small, with research primarily confined to a niche group fascinated by the C. elegans model. However, as the implications of microRNA research became clearer, the community expanded, attracting interest from scientists in various fields, including oncology, neurology, and developmental biology. Conferences that once drew a handful of attendees now regularly attract hundreds, a testament to the importance and growth of this research area.
This increasing interest signifies a shift in focus towards the broader understanding of RNA biology. As more scientists enter the field, the collaborative efforts and shared knowledge foster innovations that drive the next generation of research. The microRNA community is now a vibrant ecosystem where interdisciplinary approaches flourish, ultimately benefiting global health outcomes.
The Future of microRNA in Therapeutics and Medicine
The future of microRNA research holds tremendous promise as scientists continue to explore its multifaceted roles in human health. Current developments in therapies based on microRNAs indicate a significant leap toward targeted treatments for various diseases. This evolving landscape is likely to lead to personalized medicine approaches, paving the way for more effective and less invasive treatment options.
As research progresses, we anticipate that the elucidation of microRNA pathways will reveal new therapeutic targets, enhancing our arsenal against challenging diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative conditions. The integration of microRNA science into clinical practice represents an exciting frontier, highlighting the transformative potential of foundational research conducted by pioneers like Gary Ruvkun.
Policy Considerations for Sustaining RNA Research
As scientific advancements in RNA research continue to unfold, it is essential to consider policies that sustain and promote ongoing research efforts. Federal funding has long been the bedrock of groundbreaking discoveries, enabling scientists to pursue innovative projects. Policymakers must recognize the long-term benefits of investing in RNA research, not just for scientific advancement but for economic development and public health.
Sustaining robust funding will ensure that young scientists like those in Ruvkun’s lab do not shy away from pursuing careers in research. It is vital to foster an environment where scientific inquiry thrives, as this is where the next wave of medical breakthroughs and technological innovations are born. Supporting policies that favor scientific research investment will ultimately enhance the quality of life for individuals globally.
MicroRNA’s Role in Understanding Genetic Diseases
The exploration of microRNAs has unveiled critical insights into the molecular underpinnings of numerous genetic diseases. By elucidating how these small RNAs regulate gene expression, researchers can identify the disruptions that lead to various ailments. This understanding not only aids in the diagnosis of genetic conditions but also in the development of targeted therapies aimed at correcting these regulatory flaws.
The implications for genetic disease research are profound. With approximately 1,000 microRNAs identified in the human genome, the potential for new avenues of investigation is vast. Researchers are continuously mapping the relationships between specific microRNAs and disease phenotypes, paving the way for personalized therapeutic interventions that can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did Gary Ruvkun play in the discovery of microRNA and its implications for gene regulation?
Gary Ruvkun is a key figure in the field of microRNA research, having co-discovered microRNA in 1992 alongside Victor Ambros. Their work unveiled a crucial mechanism of gene regulation in the model organism C. elegans, which later earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. This discovery has profound implications, showing that microRNAs regulate gene expression not just in worms, but also in higher organisms, including humans.
How has federal funding supported microRNA research and its development into clinical applications?
Federal funding has been instrumental in advancing microRNA research, with Gary Ruvkun noting that about three-quarters of his lab’s research has been supported by government grants over 40 years. This investment has facilitated the exploration of microRNAs and their potential in developing therapies for serious conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s, which are now in clinical trials.
What current clinical applications are being explored in microRNA research?
MicroRNA research is being applied in clinical trials for various diseases, including heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s disease, and Alzheimer’s. These applications leverage the regulatory roles of microRNAs in gene expression to create innovative therapeutic strategies aimed at effectively treating these conditions.
How does microRNA research reflect the evolution of scientific funding and innovation?
MicroRNA research exemplifies the long-term impact of scientific funding on innovation. Gary Ruvkun’s discoveries, initially met with skepticism, gained traction largely due to sustained support from federal funding, leading to the formation of successful biotechnology companies like Alnylam. This highlights how investment in research can drive economic and scientific advances.
What challenges does microRNA research face in terms of funding and career opportunities?
Despite the breakthroughs in microRNA research, challenges remain, particularly in securing sustainable funding and ensuring career opportunities in science. Gary Ruvkun emphasizes concerns that diminishing federal support may discourage young scientists from pursuing research careers in the U.S., as they might seek more stable roles abroad.
Why are microRNAs significant in the regulation of gene expression in humans?
MicroRNAs play a vital role in gene regulation by controlling the expression of protein-coding genes. Research indicates that there are approximately 1,000 microRNAs in the human genome that collectively regulate a majority of human proteins, making them essential for developing and maintaining various biological processes.
What impact has Gary Ruvkun’s microRNA research had on the scientific community and pharmaceutical industry?
Gary Ruvkun’s research on microRNA has not only transformed our understanding of gene regulation but also significantly impacted the pharmaceutical industry. His foundational discoveries paved the way for the establishment of companies focusing on RNA therapies, leading to advancements in treatments for genetic diseases.
How did the discovery of microRNA contribute to the understanding of evolutionary biology?
The discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros sparked interest in its evolutionary significance by demonstrating that these tiny RNAs are present across various species, including plants and animals. This revelation suggested that microRNAs have conserved roles in gene regulation, which contributed to broader discussions within evolutionary biology.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA while studying C. elegans, which led to their eventual Nobel Prize in 2024. |
| Funding for Research | The research was primarily funded by the NIH, with Ruvkun noting that federal funding has historically supported about three-quarters of his lab’s research. |
| Impact on Medicine | Research on microRNAs has led to therapies for diseases such as heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s disease, and Alzheimer’s, now in clinical trials. |
| Scientific Community Recognition | Initial reception was lukewarm, but interest in RNA research grew significantly over the decades as the roles of microRNAs in various organisms became evident. |
| Economic Contributions | Ruvkun’s research contributed to the formation of successful companies like Alnylam, focusing on RNA therapeutics. |
| Concerns over Future Funding | Ruvkun expresses concern that cuts to federal funding could deter young scientists from pursuing research. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has transformed our understanding of gene regulation and its implications in health and disease. The pioneering discoveries by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros showcase the critical role of microRNAs across species and their potential in developing treatments for several serious illnesses. As we stand on the brink of new therapeutic possibilities, sustaining support for microRNA research is essential for continued innovation and scientific advancement.